Lung cancer awareness month UK
Lung cancer awareness month UK
November is Lung Cancer Awareness month and is a great opportunity to stub out that last cigarette for good and make a change that will lead to a healthier, wealthier and more fulfilling lifestyle. One You Merton offers support to those interested in stopping smoking.
How common is lung cancer?
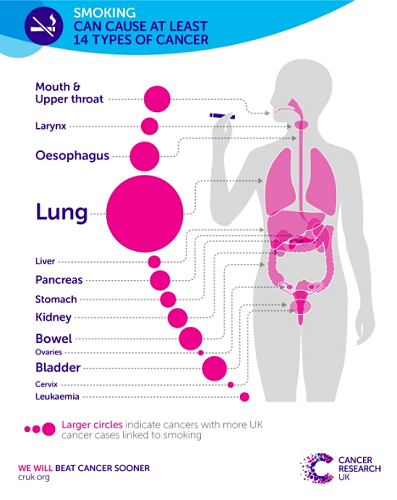
Every year 46,400 people are diagnosed with lung cancer and it is the third most common cancer in the UK. 86% of those people with lung cancer were smokers or are still smoking.
Where does lung cancer start?
Lung cancer can start in any part of the lungs or airways. These are part of the breathing system (also called the respiratory system). The breathing system includes:
- The nose and mouth
- Windpipe (trachea)
- Airways to each lung (left and right bronchus)
- lungs
Cancer that starts in the lung is called primary lung cancer. If cancer spreads to your lungs from somewhere else in your body, this is called secondary lung cancer.
There are different types of primary lung cancer and they are divided into 2 main groups:
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
About 12 out of every 100 lung cancers diagnosed are this type (12%). It is usually caused by smoking. These cancers tend to spread quite early on.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
About 87 out of 100 lung cancers in the UK (87%) are non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
What are the symptoms of lung cancer?
The most common symptoms and signs of lung cancer are:
- Chronic cough lasting more than 3 weeks
- Coughing up blood, or flecks of blood, in phlegm
- Losing weight for no reason
- Being out of breath for no reason
- Not feeling hungry
- Fatigue
- Pain in the chest
- Pain in the bone
What does smoking do to the lungs?
Smoking damages the airways as they becomes inflamed and the little hair like structures, called cilia that usually move back and forth to sweep the particles out of the airways will stop working normally. The large airways will produce more mucus which can cause a chronic cough and lead to chronic bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Smoking causes lung function to decline quickly and the impact from continuing to smoke significantly reduces the benefits of any treatment that is prescribed for the lung condition. Stopping smoking is the most beneficial intervention that is known to reduce the rate of decline of lung function.
What are the benefits to the lungs of quitting smoking?
One of the most positive steps any smoker who has lung conditions can take towards improving their health is by giving up smoking as part of managing the condition.
Research has shown that quitting smoking can bring many benefits specific to people with lung conditions:
- Lung function can improve and carbon monoxide levels return to normal in 24 hours
- Many symptoms, including shortness of breath and wheeze, may well become less severe, smokers with asthma need to use less inhaler medication
- Overall health will improve
- Prone less to chest infections
- Less likely to develop different types of cancer including lung cancer
- If a smoker has lung cancer, they are will less like to experience complications with the treatment, including radio therapy, chemotherapy, and surgery
- Slows the decline of the lung functions
How can you get help if you want to quit smoking?
To find out about about our stop smoking support visit our Quit Smoking page or you can call us on 020 8973 3545 or email us at oneyou.merton@nhs.net One of our health advisors will take you through some screening questions to see what help you are eligible for and then go through your support options.
Minel Shah
Stop Smoking Specialist
Blog cover image courtesy of Cancer Research UK
View posts by category: